Flowers are the reproductive structures of a flowering plant. They are the primary structures used in grouping plant families.
Function
- Reproduction begins with pollination and fertilization.
- Advertisement and rewards to lure a pollinator.
- Horticultural uses
- Aesthetic qualities
- Cut flowers and potted blooming plants
- Edible flowers and herbs
- Plant identification[/column][/columns]
Structure
- Pistil – Central female organ of the flower. It is generally bowling-pin-shaped and located in the center of the flower.
- Stigma – Receives pollen, typically flattened and sticky
- Style – Connective tissues between the stigma and the ovary
- Ovary – Contains ovules or embryo sacs
- Ovules – Unfertilized, immature seeds
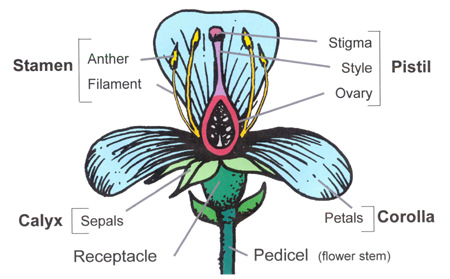
- Stamen – Male flower organ
- Anthers – pollen-producing organs
- Filament – Stalk supporting anthers
- Petals – Usually, colorful petal-like structures make up the "flower," collectively called the corolla. They may contain perfume and nectar glands.
- Sepals – Protective leaf-like enclosures for the flower buds, usually green, collectively called the calyx. Sometimes highly colored like the petal as in iris.
- Receptacle – Base of the flower
- Pedicel – Flower stalk of an individual flower in an inflorescence
Source: colostate.edu
Links
- Plantpedia: Browse flowering plants by Scientific Name, Common Name, Genus, Family, USDA Hardiness Zone, or Origin

