A Hardiness Zone is a geographically defined area in which a specific category of plant life is capable of growing, as defined by climatic conditions, including its ability to withstand the minimum temperatures of the zone. First developed for the United States by the Department of Agriculture (USDA), the use of the zones has been adopted by other nations.
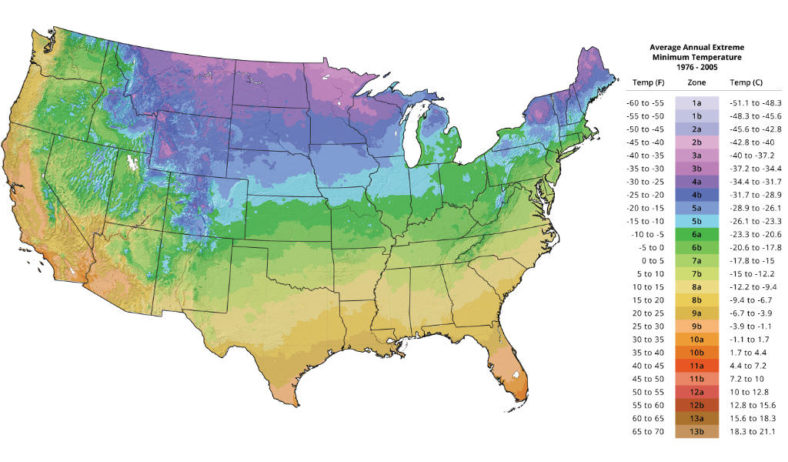
Zone 0a: below −65 °F (−53.9 °C)
Zone 0b: from −65 °F (−53.9 °C) to −60 °F (−51.1 °C)
Zone 1a: from −60 °F (−51.1 °C) to −55 °F (−48.3 °C)
Zone 1b: from −55 °F (−48.3 °C) to −50 °F (−45.6 °C)
Zone 2a: from −50 °F (−45.6 °C) to −45 °F (−42.8 °C)
Zone 2b: from −45 °F (−42.8 °C) to −40 °F (−40 °C)
Zone 3a: from −40 °F (−40 °C) to −35 °F (−37.2 °C)
Zone 3b: from −35 °F (−37.2 °C) to −30 °F (−34.4 °C)
Zone 4a: from −30 °F (−34.4 °C) to −25 °F (−31.7 °C)
Zone 4b: from −25 °F (−31.7 °C) to −20 °F (−28.9 °C)
Zone 5a: from −20 °F (−28.9 °C) to −15 °F (−26.1 °C)
Zone 5b: from −15 °F (−26.1 °C) to −10 °F (−23.3 °C)
Zone 6a: from −10 °F (−23.3 °C) to −5 °F (−20.6 °C)
Zone 6b: from −5 °F (−20.6 °C) to 0 °F (−17.8 °C)
Zone 7a: from 0 °F (−17.8 °C) to 5 °F (−15 °C)
Zone 7b: from 5 °F (−15 °C) to 10 °F (−12.2 °C)
Zone 8a: from 10 °F (−12.2 °C) to 15 °F (−9.4 °C)
Zone 8b: from 15 °F (−9.4 °C) to 20 °F (−6.7 °C)
Zone 9a: from 20 °F (−6.7 °C) to 25 °F (−3.9 °C)
Zone 9b: from 25 °F (−3.9 °C) to 30 °F (−1.1 °C)
Zone 10a: from 30 °F (−1.1 °C) to 35 °F (+1.7 °C)
Zone 10b: from 35 °F (+1.7 °C) to 40 °F (+4.4 °C)
Zone 11a: from 40 °F (+4.4 °C) to 45 °F (+7.2 °C)
Zone 11b: from 45 °F (+7.2 °C) to 50 °F (+10 °C)
Zone 12a: from 50 °F (+10 °C) to 55 °F (+12.8 °C)
Zone 12b: from 55 °F (+12.8 °C) to 60 °F (15.6 °C)
Zone 13a: from 60 °F (+15.6 °C) to 65 °F (+18.3 °C)
Zone 13b: from 65 °F (+18.3 °C) to 70 °F (21.1 °C)
Links
- Plantpedia: Browse flowering plants by Scientific Name, Common Name, Genus, Family, USDA Hardiness Zone, or Origin

